Regulation refers to “controlling human or societal behaviour by rules or regulations or alternatively a rule or order issued by an executive authority or regulatory agency of a government and having the force of law”. Regulation covers all activities of private or public behaviour that may be detrimental to societal or governmental interest but its scope varies across countries. It can be operationally defined as “taxes and subsidies of all sorts as well as explicit legislative and administrative controls over rates, entry, and other facets of economic activity”.
Definition –
Regulatory Governance can be defined as the furthering of public goals by setting, monitoring, and enforcement of regulations directed at influencing behavior and that involves private parties.
There are some ambiguity in these two terms as perceived by many people.
Some more or less conceive of ‘regulation’ and ‘governance’ as synonyms. In this sense, regulation and governance both refer to operations aimed at influencing public goals. Others argue that regulation is only a subset of activities that is encompassed with the overarching term governance. They distinguish regulation from the granting, allocating and distributing of scarce resources. While regulation only indirectly shapes the distribution of scares resources in society by setting, monitoring and enforcing norms and standards, other policies are about the direct distribution or redistribution of scarce resources.In this sense, governance refers to both direct and indirect attempts to achieve public goals by way of ‘providing, distributing, and regulating’.
All contributions deal with setting, monitoring and enforcing norms and standards. Hence, It can be limited the analysis to governancy by regulation and leave out of consideration the subcategory of governance that concerns the direct distribution or redistribution of scarce resources.
The second difference in meanings attributed to governance pertains to the relationship between governance and government. Some distinguish governance from contents and actors. Conceived of as such governance concerns modes of social coordination to provide collective goods by regulation regardless of which actors undertake these attempts. According to this definition, governance can also include hierarchical steering by state actors only. Others define governance in terms of the involvement of private parties with the realization of public goals, or ‘beyond government’. Conceived of as such, governance is distinguished from social steering by state agents only, or ‘governance by government’.
Important Regulatory Bodies in India
- RBI – Reserve Bank of India
Sector: Banking & Finance, Monetary Policy
- SEBI – Securities and Exchange Board of India
Sector: Securities (Stock) & Capital Market
- IRDAI – Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority
Sector: Insurance
- PFRDA – Pension Fund Regulatory & Development Authority
Sector: Pension
- NABARD – National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
Sector: Financing Rural Development
- SIDBI – Small Industries Development Bank of India
Sector: Financing Micro, Small and Medium-Scale Enterprises
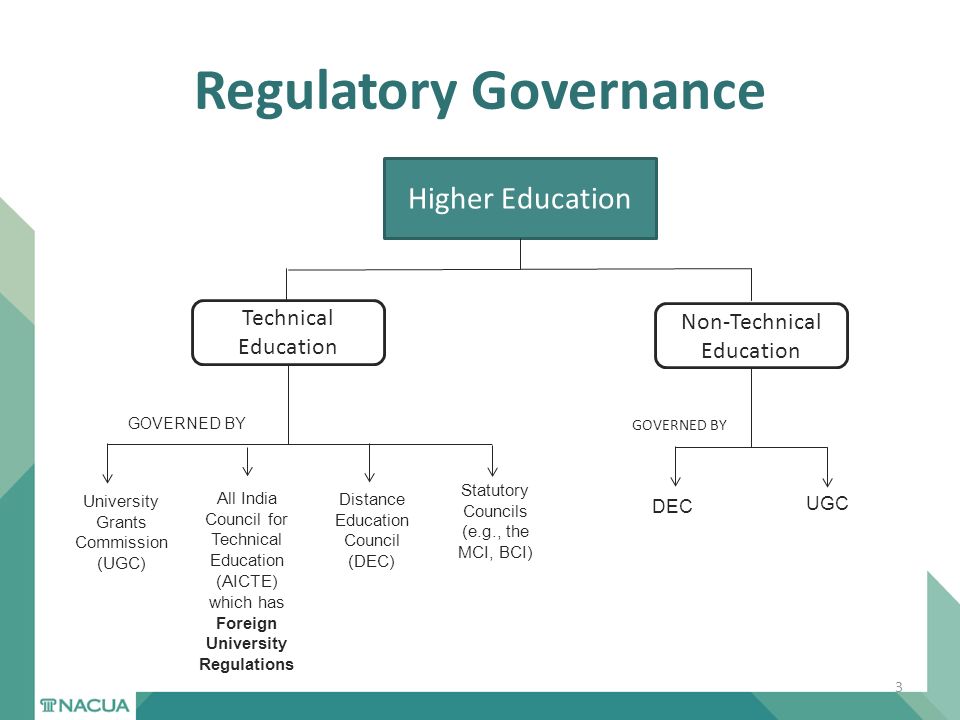
Example – Regulatory Governance in Education à